Introduction
Biopsies are a crucial part of modern medicine, playing a vital role in diagnosing and monitoring various health conditions. But what is a biopsy, and why are they so important? In this guide, we’ll explore the different types of biopsy tests, providing clear and concise information to help you understand their significance and processes.
1. What is a Biopsy?
A biopsy is a medical test where a small sample of tissue or cells is taken from the body for examination under a microscope. The primary purpose of a biopsy is to diagnose diseases, such as cancer, or to assess the severity of a condition.
2. Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA)
Description: FNA is a minimally invasive biopsy procedure where a thin, hollow needle is used to extract a small amount of tissue or fluid. Uses: Commonly used for lumps or masses found in the neck, thyroid, or breasts. Procedure: The needle is inserted into the target area, and a sample is drawn out. Pros and Cons: It’s quick and usually requires no anesthesia, but may not provide enough tissue for a definitive diagnosis.
3. Core Needle Biopsy
Description: A core needle biopsy uses a larger needle to remove a core of tissue. Uses: Often used for breast, prostate, and liver biopsies. Procedure: A larger needle is used to extract a cylindrical sample of tissue. Pros and Cons: Provides more tissue than FNA, which can lead to a more accurate diagnosis, but it is slightly more invasive.
4. Excisional and Incisional Biopsies
Excisional Biopsy:
- Description: The entire lump or suspicious area is removed.
- Uses: Typically used when a lesion is small enough to be removed completely.
- Procedure: Surgical removal of the whole area of concern.
- Pros and Cons: Can provide a definitive diagnosis but requires more recovery time.
Incisional Biopsy:
- Description: Only a portion of the abnormal tissue is removed.
- Uses: Used when the lesion is too large to be removed entirely.
- Procedure: Surgical removal of a part of the suspicious area.
- Pros and Cons: Less tissue is removed compared to excisional biopsy, which may sometimes be insufficient for diagnosis.
5. Endoscopic Biopsy
Description: This biopsy is performed using an endoscope, a flexible tube with a camera and tools. Uses: Commonly used for gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract, and urinary tract biopsies. Procedure: The endoscope is inserted into the body, and a tool at the end is used to take a tissue sample. Pros and Cons: Minimally invasive with a direct visual guide, but may require sedation.
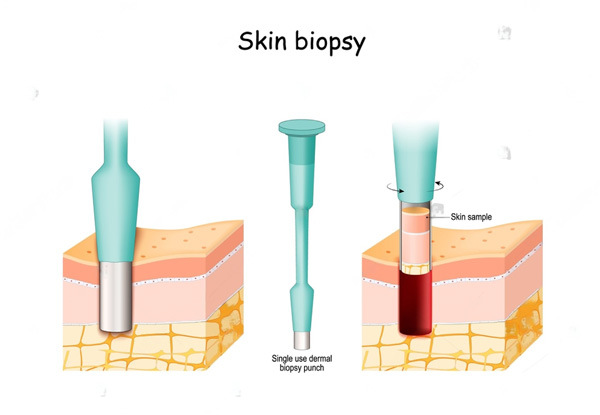
6. Skin Biopsy
Description: There are three main types: shave, punch, and excisional biopsies.
- Shave Biopsy: Removes a thin layer of skin.
- Punch Biopsy: Removes a deeper, circular section of skin.
- Excisional Biopsy: Removes a whole lump or aberrant region. Uses: Used to diagnose skin conditions, including cancers. Procedure: Depending on the type, a razor, punch tool, or scalpel is used. Pros and Cons: Provides a good sample for diagnosis with minimal discomfort.
7. Bone Marrow Biopsy
Description: A bone marrow biopsy involves taking a sample from the bone marrow, usually from the hip bone. Uses: Diagnoses blood disorders and cancers like leukemia. Procedure: A needle is inserted into the bone to extract marrow. Pros and Cons: Provides critical information about blood and marrow diseases but can be painful and requires local anesthesia.
8. Liquid Biopsy
Description: A liquid biopsy analyzes blood or other bodily fluids to detect cancer cells or fragments of tumor DNA. Uses: Especially useful in monitoring cancer and detecting mutations. Procedure: A simple blood draw is usually all that’s needed. Pros and Cons: Non-invasive and quick, but may not detect all types of cancer.
9. Preparing for a Biopsy
Before undergoing a biopsy, it’s important to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully. This may include fasting, avoiding certain medications, and arranging for someone to drive you home if sedation is used.
10. Aftercare and Recovery
After your biopsy, take care to follow all post-procedure instructions. This may include keeping the biopsy site clean, avoiding strenuous activities, and monitoring for signs of infection.
Conclusion
Biopsies are invaluable tools in modern medicine, providing essential insights into various health conditions and aiding in accurate diagnoses. From the minimally invasive Fine Needle Aspiration to the comprehensive Excisional Biopsy, each type of biopsy has unique applications, advantages, and limitations. Understanding these differences can help demystify the process and alleviate some of the anxiety associated with medical procedures.
For those seeking top-notch diagnostic services, Midas Care Clinic, the best diagnostic center in Vasai, offers a range of biopsy tests with expert care. Whether you need a biopsy test in Vasai or a biopsy test in Virar, Midas Care Clinic provides comprehensive and professional services to meet your diagnostic needs.

