Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding Prostate Conditions
- What is Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE)?
- What is Traditional Prostate Surgery?
- Comparing PAE and Traditional Surgery
- Suitability for Patients
- Preparing for Treatment
- Aftercare and Recovery
- Conclusion
- FAQs
1. Introduction
Prostate health issues, particularly benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), are common among men as they age. These conditions can significantly impact quality of life, prompting a range of treatment options. Among the latest advancements is Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE), a minimally invasive procedure that offers an alternative to traditional surgery. In this blog, we will compare Prostate Artery Embolization with traditional surgical methods to help you determine which might be better for your needs.
2. Understanding Prostate Conditions
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland that affects many men as they age. Symptoms include frequent urination, difficulty starting urination, and a weak urine stream. These issues can disrupt daily life and lead to further complications if left untreated.
3. What is Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE)?
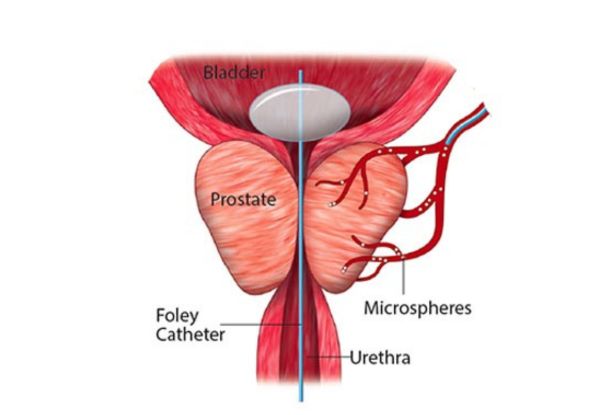
Definition: Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE) is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat BPH.
Procedure: During PAE, a radiologist inserts a catheter through a small incision in the groin or wrist and threads it to the prostate arteries. Tiny particles are then injected to prevent blood flow to the prostate and cause it to shrink.
Benefits: PAE offers several advantages, including reduced recovery time, less pain compared to traditional surgery, and a lower risk of complications. It also preserves erectile function and urinary continence in many cases.
Risks and Limitations: While PAE is generally safe, potential risks include infection, bleeding, and the need for a follow-up procedure if symptoms persist.
For those seeking Prostate Artery Embolization in Vasai, many local medical centers now offer this cutting-edge treatment.
4. What is Traditional Prostate Surgery?
Definition: Traditional prostate surgery includes procedures like Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) and Open Prostatectomy.
Procedure:
- TURP: A thin tube (resectoscope) is inserted through the urethra to remove excess prostate tissue.
- Open Prostatectomy: Involves a larger surgical incision to remove part or all of the prostate gland.
Benefits: These surgeries can provide significant relief from symptoms and are often considered when other treatments fail. TURP, in particular, has a long history of effectiveness.
Risks and Limitations: Traditional surgeries can be more invasive, leading to longer recovery times, potential for more pain, and risks of complications such as incontinence or sexual dysfunction.
5. Comparing PAE and Traditional Surgery
Effectiveness: Both PAE and traditional surgery are effective at relieving symptoms of BPH. PAE is less invasive and may be preferred for patients who are at higher risk for surgical complications.
Recovery Time: PAE typically offers a faster recovery, with many patients resuming normal activities within a few days. In contrast, traditional surgeries may require several weeks for full recovery.
Side Effects: PAE generally has fewer side effects, including reduced risk of sexual dysfunction and incontinence compared to traditional surgery.
Long-Term Outcomes: Both treatments can be effective long-term solutions, though PAE is a newer technique with ongoing studies to confirm its long-term efficacy.
6. Suitability for Patients
Who Benefits from PAE? PAE is suitable for patients who prefer a less invasive approach or those who may not be ideal candidates for surgery due to other health conditions.
Who Benefits from Traditional Surgery? Traditional surgery may be more appropriate for patients with severe BPH symptoms or those who have not responded well to other treatments.
Decision Factors: Patients should consider factors such as overall health, the severity of symptoms, and personal preferences when choosing between PAE and traditional surgery.
7. Preparing for Treatment
Pre-Treatment Considerations: Patients should follow pre-treatment instructions provided by their healthcare provider, which may include dietary restrictions, medication adjustments, and arranging for post-procedure care.
Questions to Ask Your Doctor: Important questions to ask include:
- What are the potential benefits and risks of each treatment option?
- How long is the recovery period?
- What are the expected outcomes for my specific condition?
8. Aftercare and Recovery
PAE Aftercare: Post-PAE care typically involves managing minor discomfort and following up with your doctor to monitor progress, Most patients have a rather speedy recovery.
Traditional Surgery Aftercare: Recovery from traditional surgery requires more time and involves managing pain, preventing complications, and following specific post-operative care instructions.
Monitoring and Follow-Up: Regular follow-up appointments are crucial for both treatments to ensure healing and address any ongoing symptoms.
9. Conclusion
Both Prostate Artery Embolization and traditional prostate surgery offer effective treatment options for BPH. The choice between them depends on individual health conditions, personal preferences, and the advice of your healthcare provider. Consulting with a specialist can help you make an informed decision that best suits your needs.

