Biopsies do not cause cancer to spread in most cases. Medical studies show that the risk is extremely low. Biopsies help detect cancer early and guide proper treatment.
Introduction
It’s common for people to feel uneasy about certain medical procedures, especially when the word cancer is involved. One concern that often comes up is this: do biopsies spread cancer? It’s a question many ask, and it’s important to address it with clear, reliable information.
The idea that cancer might spread because of a biopsy can cause hesitation or fear, which may lead to delays in getting a proper diagnosis.
Let’s be clear. This content is here to explain things in a straightforward way, so you can understand what a biopsy really is, how it works, and whether this concern holds any truth. When making choices about your health, especially something as serious as cancer, it helps to have facts you can trust.
Some might wonder, can a biopsy spread cancer, or ask, is biopsy dangerous? These are valid questions. After all, nobody wants to take unnecessary risks, especially when it comes to something as important as diagnosing or ruling out cancer.
What is a Biopsy?
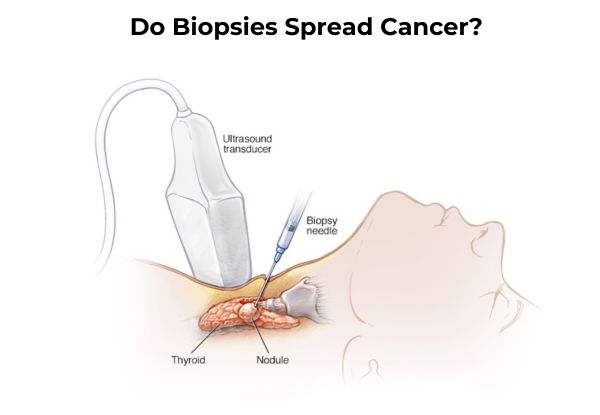
A biopsy is a type of diagnostic test that helps doctors understand what’s happening inside the body. It involves taking a small tissue sample from an area that looks unusual or where there’s a concern, such as a lump or growth. The goal is to check if the cells in that area are normal or if there’s any sign of disease, including cancer.
This procedure plays a major role in cancer diagnosis because it gives doctors a clear look at the cells under a microscope. Without this step, it can be difficult to know for sure whether a condition is harmless or needs treatment.
There are different ways to perform a biopsy:
- A needle biopsy uses a thin needle to collect the sample.
- A surgical biopsy involves making a small cut to remove part of the tissue.
- An endoscopic biopsy uses a flexible tube with a camera to reach internal areas.
These methods are chosen based on where the tissue is located and what information the doctor needs. For those in need of a biopsy test in Mumbai, it’s important to know that experienced professionals, such as those at Midas Care Clinic, follow safe and reliable methods for testing.
Why Do People Think Biopsies Spread Cancer?
Many people feel uneasy when they hear the word biopsy, especially if they or someone close to them is facing a possible cancer diagnosis. One of the most common fears is the idea that taking a sample from a tumor might cause it to spread. So, can a biopsy spread cancer? That’s a question often driven by cancer fear rather than facts.
This belief usually stems from anecdotal stories or information that’s outdated. Years ago, before medical techniques became more advanced, there were a few reports of cancer spreading after certain types of procedures.
But it’s important to understand that those cases were rare and often linked to less refined methods or specific conditions, not to the standard biopsy procedures used today.
Another reason people worry is because they imagine that physically touching or manipulating a tumor could somehow cause cancer cells to break away and travel to other parts of the body. This fear of tumor manipulation leading to spread sounds reasonable on the surface, but it doesn’t hold up when we look at modern research and medical practices.
What adds to the confusion are cancer spread myths shared in casual conversations or on unverified websites. When people hear such stories without checking the facts, it’s easy for doubts to grow. But in reality, the tools, techniques, and safety protocols used in biopsies today are designed to minimize risk and gather the right information without causing harm.
Can a Biopsy Actually Spread Cancer Cells?
Let’s address this head-on. Do biopsies spread cancer? The direct answer is no, not in the way many people fear. In modern medicine, the risk of cancer spreading because of a biopsy is extremely low. This concern often comes from a misunderstanding of rare situations that don’t reflect how biopsies are performed today.
There is a medical term called needle tract seeding. It refers to a situation where cancer cells might spread along the path where a needle was inserted during a biopsy. While this has happened in some cases, it’s very rare, and usually tied to certain types of tumors, like liver or kidney cancers, and even then, only in specific circumstances. Most types of biopsy procedures are not linked to this issue at all.
Doctors take many biopsy safety measures to prevent any risk. They use precise tools, follow strict guidelines, and are trained to collect the tissue sample in a way that avoids problems. The area is carefully chosen, the tools are sterilized, and if needed, imaging technology helps guide the procedure. These steps help make sure the process is as safe and effective as possible.
So when people ask, can a biopsy spread cancer, they’re often thinking about old risks that don’t match up with how procedures are done today. In fact, without a biopsy, doctors would be guessing instead of knowing. A biopsy provides answers, and with the safety protocols in place, it offers information that helps guide treatment without adding unnecessary risk.
Does Cancer Spread Faster After Biopsy?
Some people notice that their condition seems to change after a biopsy, and it leads to a common question: does cancer spread faster after biopsy? The short answer is no. A biopsy does not cause tumor growth rate to increase or make cancer progress more quickly.
This belief often comes from personal stories where people noticed symptoms worsening after their procedure, but this is not caused by the biopsy itself.
What usually happens is that biopsy and cancer progression are linked in time, but one does not cause the other. In many cases, the cancer was already advancing, and the biopsy simply helped doctors confirm it. It’s easy to connect the two events, the biopsy and the changes noticed afterwards but this is a situation where correlation isn’t causation.
Clinical research supports this. Studies have found that biopsies do not increase cancer spread or speed.
People might feel that things changed quickly after their biopsy because that’s when their cancer was diagnosed and they became more aware of symptoms. However, the biopsy itself doesn’t trigger faster growth, it simply brings clarity about what’s already happening in the body.
Is Biopsy Dangerous?
Many people ask, is biopsy dangerous, especially when they are advised to undergo one for a possible diagnosis. It’s natural to feel cautious about any medical procedure, and a biopsy test is no exception. The truth is, while no procedure is completely free of risk, biopsies are generally safe when done under proper medical supervision.
There are some minor complications that can occur, but they are not common and are not related to cancer spread. These might include mild bleeding, bruising, or a small chance of infection at the site where the tissue is collected. In most cases, these issues are temporary and can be managed easily with basic care.
Doctors always consider the risk-benefit analysis before recommending a biopsy. The small risks involved are far outweighed by the benefits, especially when it comes to understanding what’s really going on inside the body.
Without a biopsy, it can be hard to know whether a condition is serious or not. Getting the right diagnosis means treatment can begin at the right time, and that can make a big difference in the outcome.
While there is a small chance of minor issues, a biopsy test is a valuable tool in medicine that helps both doctors and patients make informed decisions. It’s one of the most reliable ways to understand what’s happening in the body and to plan the best path forward.
What Does Research Say About Biopsy Safety?
Understanding the safety of biopsy procedures is crucial for patients and healthcare providers alike. Recent studies from reputable medical institutions offer valuable insights:
- Prostate Biopsy Approaches: A comprehensive meta-analysis compared two common methods of prostate biopsy: transperineal (TP) and transrectal (TR). The findings indicated that the TP approach had a significantly lower risk of post-procedural infections, with only a 1% infection rate compared to 3.5% in the TR approach. This suggests that the TP method may offer enhanced safety concerning infections.
- Ultrasound-Guided Core Needle Biopsy for Lymphoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis assessed the diagnostic performance and safety of ultrasound-guided core needle biopsies in patients with lymphoma. The study reported a high diagnostic accuracy with a sensitivity of 94% and a specificity of 100%. The complication rate was low, at 1%, with most complications being self-limiting.
- Esophageal Biopsies During Endoscopy: Research evaluating the safety of performing esophageal biopsies during upper endoscopy for food impaction found that biopsies were unlikely to cause adverse events. Specifically, only 2.7% of patients who underwent biopsies experienced adverse events, none of which were related to the biopsy procedure itself.
- MRI-Informed Biopsy Decision-Making: A cohort study investigated the oncological safety of using prebiopsy magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to inform biopsy decisions in men with suspected prostate cancer. The study concluded that men with negative MRI results who avoided immediate biopsy were not at elevated risk of clinically significant prostate cancer, confirming the safety of this approach when appropriate monitoring is in place.
These findings underscore that, while minor complications can occur, biopsy procedures are generally safe. Advancements in medical techniques and careful patient selection have further minimized risks, making biopsies a reliable tool for accurate diagnosis.
When Might There Be a Risk?
While biopsies are considered safe in most cases, some people wonder about situations where the cancer cells spreading risk might be slightly higher. The truth is, this is very uncommon, but it’s helpful to understand when certain factors might lead doctors to take extra precautions.
In rare situations, biopsy-related risks may be slightly increased, depending on the specific cancer types involved. For instance, in certain liver cancers or kidney cancers, there have been a few reports of a process called needle tract seeding. This refers to a situation where a small number of cancer cells might attach to the needle pathway during a biopsy and potentially settle in nearby tissue.
It’s important to know that even in these rare instances, the overall chance of this happening is still very low. In fact, improvements in biopsy techniques and safety measures have made this issue even less common today than in the past.
Doctors are aware of these possibilities and consider them when planning the biopsy. They may use different techniques or approaches depending on the location of the tumor and other patient concerns.
For most people, these situations will not apply. Biopsies remain a safe and effective way to find out what’s happening inside the body and to make informed choices about care. Understanding the rare exceptions helps give a full picture, but it’s just as important to focus on how small the risks are in comparison to the benefits of getting an accurate diagnosis.
Conclusion
If you’ve ever wondered, do biopsies spread cancer, the answer is clear. With today’s medical standards, safe biopsy procedures are widely practiced, and the risk of cancer spread is extremely low. This concern, though common, is based more on outdated fears than current medical evidence.
Biopsies play an essential role in early diagnosis, helping doctors detect conditions at a stage when treatment is most effective. Without a biopsy, reaching a confident diagnosis becomes more difficult, which can delay proper care. For this reason, the benefits of a biopsy far outweigh the minor risks involved.
Still, it’s understandable to have questions. That’s why it’s important to speak with a qualified doctor who can provide healthcare advice tailored to your situation. At Midas Care Clinic, experienced professionals offer safe biopsy procedures and guide patients through each step with care and accuracy.
Informed decisions begin with accurate information. A biopsy is not just a test. It’s a tool that helps doctors and patients move forward with clarity and confidence.
FAQs
Q1: Can a biopsy cause cancer cells to move?
Ans: This concern is common, but in reality, biopsy risk factors for cancer spread are minimal. When done correctly, a biopsy does not cause cancer cells to travel or move to other parts of the body. Modern techniques are designed to prevent this outcome.
Q2: Is it better to avoid biopsy if cancer is suspected?
Ans: Avoiding a diagnosis procedure like a biopsy can delay treatment planning. Without a biopsy, doctors may not have the full picture needed to decide the best course of action. The benefits of getting clear results far outweigh the small risks involved.
Q3: What is needle tract seeding and should I be worried?
Ans: Needle tract seeding is a rare occurrence where cancer cells attach along the path of the biopsy needle. This has been documented in a few specific cancers like liver or kidney, but overall, it is very uncommon. Doctors take steps to reduce this already low risk.
Q4: How often does cancer spread after a biopsy?
Ans: Cancer spread after biopsy is extremely rare. Clinical studies show that the chance of this happening is very low, especially with the safety methods used today. Most patients experience no spread and benefit from the information a biopsy provides.
Q5: Are there safer alternatives to biopsy?
Ans:; In some cases, doctors may suggest imaging tests first. However, these cannot replace the detail gained from a biopsy test. A biopsy remains the most reliable method for confirming a diagnosis and planning the right treatment.
Q6: Does a biopsy make cancer grow faster?
Ans: There is no evidence that a biopsy makes cancer grow faster. This idea comes from situations where the cancer was already advancing, and the diagnosis procedure simply revealed it. The biopsy itself does not speed up growth.
Q7: What precautions do doctors take during biopsy?
Ans: Doctors follow strict safety steps to reduce biopsy risk factors. They use sterile equipment, precise tools, and sometimes imaging guidance to ensure the tissue sample is taken safely. These measures keep complications to a minimum.
Q8: Is biopsy painful or harmful in any way?
Ans: Most biopsies cause only mild discomfort. Depending on the type, doctors may use local anesthesia to reduce pain. Serious harm is rare, and any minor discomfort usually fades within a short time.
Q9: Should I delay biopsy due to fear of spread?
Ans: Delaying a biopsy can delay early diagnosis and treatment planning. The fear of spread is understandable but not supported by current research. Timely testing helps guide proper care and gives peace of mind.
Q10: Are there different risks for different types of biopsies?
Ans: Yes, the risks may vary slightly based on the method used. For example, a needle biopsy usually has fewer risks compared to surgical methods. Your doctor will explain the best option for your condition and how they manage safety in each case.

