Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) is a common but often overlooked condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when arteries in the legs become narrowed or blocked, reducing blood flow. If left untreated, this could cause major issues. Understanding the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for PAD is essential for anyone concerned about their vascular health.
What is Peripheral Artery Disease?
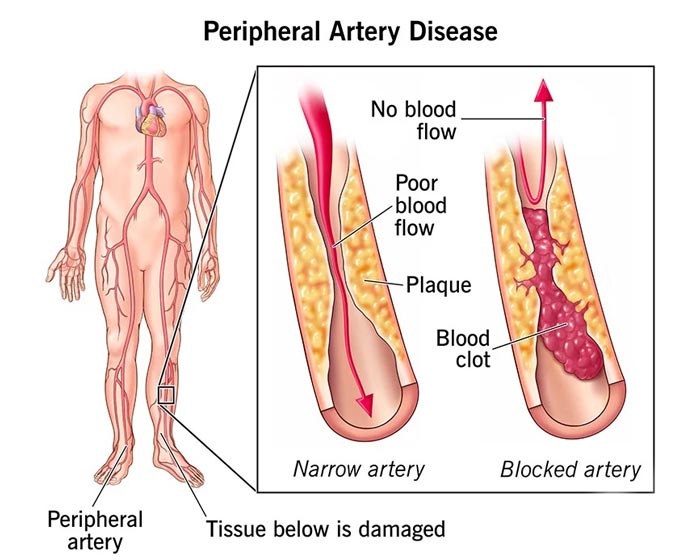
PAD is a circulatory problem where narrowed arteries reduce blood flow to the limbs, most often the legs. The primary cause of PAD is atherosclerosis, where fatty deposits (plaque) build up in the artery walls. This narrowing can lead to serious health issues, including heart attack and stroke. Risk factors include age, smoking, diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol levels. People over 50, especially those with these risk factors, should be particularly aware of PAD.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Knowing the symptoms of PAD is crucial for early detection and treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Leg Pain or Cramping: Many people experience pain, cramping, or heaviness in the legs or buttocks during physical activities, such as walking or climbing stairs. This condition is known as intermittent claudication and usually eases with rest.
- Weak or Absent Pulses: You may notice weak or absent pulses in your legs or feet, indicating poor blood flow.
- Numbness or Weakness: Some people may have weakness or numbness in their legs, which makes walking challenging.
- Coldness in the Lower Leg or Foot: If one leg or foot feels colder than the other, it could be a sign of reduced blood flow.
- Color Changes: Legs or feet may appear pale, bluish, or have a shiny appearance, indicating circulation issues.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s essential to consult a peripheral artery disease specialist for a proper evaluation.
Diagnosis of PAD
PAD diagnosis requires a few stages. An extensive medical history and physical examination are the first steps a healthcare professional will take. In addition to evaluating your general health, they might check the pulse in your legs and feet.
The ankle-brachial index (ABI) test is a frequently used diagnostic tool for PAD. The blood pressure in your arm and ankle are compared during this test. Your ankle pressure may be lower than your arm pressure, which could be a sign of PAD. Further testing, including angiography or ultrasounds, can help see how blood flows through your arteries and spot obstructions.
For those in the Vasai area, seeking diagnosis at the best diagnostic center in Vasai can ensure accurate results and prompt referrals to specialists.
Treatment Options
If diagnosed with PAD, there are various treatment options available to improve your symptoms and overall health. Here are some common approaches:
1. Lifestyle Modifications
Making healthy lifestyle changes is often the first step in managing PAD. Here are some tips:
- Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet low in saturated fats and high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help lower cholesterol and improve overall health.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity is crucial for managing PAD. Walking, swimming, and cycling can improve circulation and reduce symptoms. A healthcare provider may recommend a supervised exercise program to help you start.
- Smoking Cessation: One of the best strategies to enhance your vascular health is to give up smoking. Smoking raises the risk of problems and destroys blood vessels.
2. Medications
In addition to lifestyle changes, your doctor may prescribe medications to help manage PAD. Common medications include:
- Blood Thinners: These medications help prevent blood clots, improving blood flow.
- Cholesterol-Lowering Drugs: Statins and other cholesterol-lowering medications can help reduce plaque buildup in the arteries.
- Medications to Improve Symptoms: Certain medications may be prescribed to help alleviate pain and improve walking distance.
3. Surgical Interventions
If lifestyle changes and medications are not sufficient, surgical options may be considered. These include:
- Angioplasty: a process that involves inserting a tiny balloon into the constricted artery and inflating it to make it wider. To maintain the artery open, a stent—a tiny mesh tube—may occasionally be inserted.
- Bypass Surgery: In more serious situations, bypass surgery can be required. This entails utilizing a vein or synthetic material to create a new channel for blood to flow around the clogged artery.
For patients seeking specialized care, visiting a peripheral artery disease specialist at facilities like Midas Care Clinic can provide tailored treatment options and expert guidance.
Living with PAD
Managing life with PAD involves regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider. It’s essential to monitor your symptoms and make adjustments to your treatment plan as needed. Staying active, following a heart-healthy diet, and keeping a positive attitude can significantly improve your quality of life.
Conclusion
Peripheral Artery Disease is a serious condition that affects many people, but it doesn’t have to control your life. By recognizing the symptoms early and seeking proper diagnosis and treatment, you can manage PAD effectively. Remember, awareness and proactive measures are your best allies in navigating this condition. If you suspect you have PAD, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional or visit the best diagnostic center in Vasai for evaluation. A healthier tomorrow can result from actions taken now.

