1. Introduction
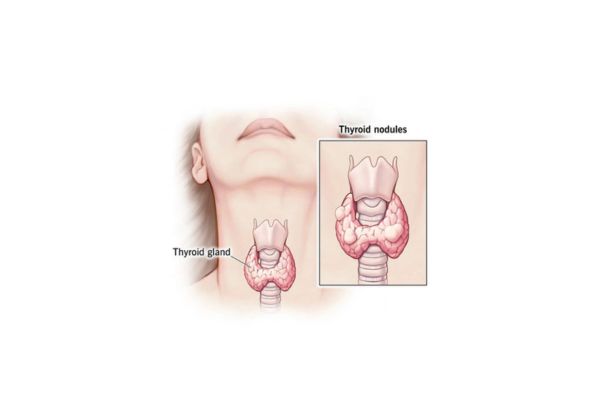
Thyroid nodules are abnormal growths or lumps that form within the thyroid gland, which is located in the neck. These nodules are relatively common and are often discovered during routine physical exams or imaging tests. While most thyroid nodules are benign (non-cancerous), some can cause discomfort or lead to other health issues, such as difficulty swallowing or changes in hormone levels.
Early detection of thyroid nodules is critical for effective management. Regular check-ups, including ultrasounds or fine needle aspiration (FNA), are essential to identify the presence of nodules and assess whether they are benign or require further investigation. Once diagnosed, treatment options must be explored based on the nodule’s size, type, and symptoms.
Among the available treatments, thyroid nodule ablation treatment is a non-surgical option gaining popularity for certain cases. This minimally invasive procedure can effectively shrink or eliminate benign thyroid nodules. However, surgery is sometimes recommended when the nodule is large, malignant, or causing significant symptoms. Choosing the right treatment, whether thyroid nodule ablation in Mumbai or surgery, depends on various factors that need careful consideration by both the patient and healthcare provider.
In the next sections, we will explore the benefits of thyroid nodule ablation over surgery and when this treatment may be a more suitable option.
2. Understanding Thyroid Nodules
Thyroid nodules are abnormal growths or lumps that develop within the thyroid gland, which is responsible for producing hormones that regulate metabolism. While most thyroid nodules are benign (non-cancerous), some may be malignant or cause other health issues. Understanding the types and characteristics of these nodules is crucial in determining the most appropriate treatment.
Definition and Types of Thyroid Nodules
A thyroid nodule is a growth or lump that forms within the thyroid gland. There are two main types of thyroid nodules:
- Solid nodules: These are dense and typically more concerning as they may sometimes contain cancerous cells.
- Cystic nodules: These are fluid-filled and usually benign, but they can also be associated with certain thyroid conditions.
In addition to these basic types, thyroid nodules can also be categorized by whether they are hot or cold based on their activity level, which can be assessed through an ultrasound. Hot nodules produce excess thyroid hormones, while cold nodules do not. Cold nodules have a higher chance of being malignant.
Symptoms and Risk Factors
In many cases, thyroid nodules do not cause noticeable symptoms. However, larger nodules can lead to symptoms such as:
- Swelling or a visible lump in the neck
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing
- Pain in the neck or throat area
- Hoarseness or changes in voice
Risk factors for developing thyroid nodules include:
- Family history of thyroid problems or cancer
- Radiation exposure, particularly during childhood
- Gender (women are more likely to develop thyroid nodules than men)
- Age (nodules are more common in older adults)
While most thyroid nodules are benign, certain risk factors, like a family history of thyroid cancer, may raise the concern for malignancy, making early diagnosis even more important.
How Thyroid Nodules Are Diagnosed
Thyroid nodules are often detected during routine physical exams or imaging studies. The following diagnostic methods are commonly used:
- Ultrasound: This imaging technique helps doctors evaluate the size, shape, and characteristics of the thyroid nodule. It also helps differentiate between solid and cystic nodules.
- Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA) Biopsy: If a nodule appears suspicious on ultrasound, a biopsy may be performed to collect a sample of cells for further examination under a microscope.
- Blood Tests: To evaluate thyroid function, blood tests can check levels of thyroid hormones (T3, T4) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). Elevated or low levels may indicate thyroid dysfunction.
For more specialized diagnostic services, you might visit a best diagnostic center in Vasai, which can provide advanced imaging and biopsy options to ensure accurate and early detection of thyroid conditions.
3. Traditional Treatment: Surgery for Thyroid Nodules
Surgery is one of the most commonly recommended treatments for thyroid nodules, especially when certain conditions or risk factors are present. While thyroid nodule ablation treatment offers a non-surgical alternative, surgery remains a widely used approach for both benign and malignant nodules.
When Surgery Is Typically Recommended
Surgery for thyroid nodules is typically recommended in the following situations:
- Malignant or suspicious nodules: If a nodule is found to be cancerous or highly suspicious for malignancy after a biopsy, surgery is usually necessary to remove the affected part of the thyroid gland or the entire thyroid.
- Large or growing nodules: When a thyroid nodule becomes large enough to cause symptoms such as difficulty swallowing, breathing, or neck pain, surgery may be required to remove the nodule and alleviate these symptoms.
- Thyroid dysfunction: Nodules that cause the thyroid gland to produce abnormal levels of hormones (hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism) may also require surgical intervention if other treatments are ineffective.
- Cosmetic concerns: In some cases, people choose surgery if the nodule is visible or cosmetically concerning, particularly if it is large or affecting the shape of the neck.
Types of Surgeries Available
There are different types of thyroid surgeries, depending on the location and extent of the nodule and whether the thyroid is affected by cancer:
- Lobectomy: This is a partial removal of the thyroid, where only the lobe containing the nodule is removed. It is typically performed when the nodule is localized to one side of the thyroid gland.
- Total thyroidectomy: In cases of thyroid cancer or larger nodules that affect both lobes of the thyroid, a total thyroidectomy is performed, which involves removing the entire thyroid gland. After this procedure, patients typically need lifelong thyroid hormone replacement therapy.
- Near-total thyroidectomy: This surgery involves the removal of most of the thyroid tissue, leaving a small portion for thyroid hormone production. It may be recommended in certain situations, such as for benign nodules with a risk of recurrence.
Each of these surgeries has its own set of advantages and risks, which must be carefully considered before making a decision.
Benefits and Risks of Surgery
Benefits of surgery include:
- Complete removal of malignant tissue: Surgery ensures that cancerous nodules are fully removed, potentially preventing the spread of cancer.
- Permanent solution for large or problematic nodules: Surgery provides a permanent solution for symptomatic nodules that cause pain or difficulty breathing and swallowing.
- Restoration of thyroid function: In cases where thyroid dysfunction is caused by the nodule, surgery can restore normal thyroid function after removal of the problematic tissue.
However, there are risks associated with surgery, such as:
- Risk of complications: Like any surgery, thyroid surgery carries risks such as infection, bleeding, or adverse reactions to anesthesia.
- Damage to surrounding structures: The thyroid is located near vital structures like the vocal cords and parathyroid glands. Surgery may inadvertently damage these areas, potentially leading to voice changes, difficulty speaking, or calcium imbalances.
- Hypothyroidism: In cases where a significant portion of the thyroid is removed (total thyroidectomy or near-total thyroidectomy), patients may develop hypothyroidism, requiring lifelong thyroid hormone replacement therapy.
While surgery is a proven and effective treatment for thyroid nodules, it is not without its risks, and patients should carefully consider these factors when weighing their treatment options. For those seeking a less invasive approach, thyroid nodule ablation in Mumbai may be a suitable alternative, particularly for benign nodules.
4. Ablation Therapy: A Modern Treatment Approach
What is Ablation Therapy?
Ablation therapy refers to a minimally invasive medical procedure used to treat thyroid nodules by destroying abnormal tissue without the need for major surgery. There are various methods of ablation, with radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and laser ablation being the most common approaches for treating thyroid nodules.
- Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) uses heat generated by radio waves to shrink or destroy thyroid nodules. The procedure involves inserting a needle-like electrode into the nodule, which emits radiofrequency energy to target and break down the abnormal tissue.
- Laser Ablation is another technique that uses focused light to generate heat, which then targets the nodule tissue to reduce its size and alleviate symptoms.
Both methods are minimally invasive and are considered alternatives to traditional surgical approaches for benign thyroid nodules.
How Ablation Works in Treating Thyroid Nodules During ablation therapy, the targeted thyroid nodule is treated by applying heat to the affected tissue. The process reduces the size of the nodule, which helps improve symptoms such as difficulty swallowing or neck discomfort. For some patients, it can also improve the cosmetic appearance of the neck by reducing the size of the nodule, which may otherwise be noticeable or unsightly.
Ablation therapy can be particularly beneficial for individuals with benign nodules who prefer a less invasive treatment. It is also considered a suitable treatment for patients who are not ideal candidates for surgery due to other health conditions.
Advantages of Ablation Over Traditional Surgery Ablation therapy offers several advantages over traditional surgical methods for thyroid nodules:
- Minimally Invasive: Unlike traditional surgery, which requires incisions and a longer recovery time, ablation therapy is performed through a small needle, reducing the risk of infection and scarring. The procedure is typically done under local anesthesia, and many patients can go home the same day.
- Faster Recovery: Recovery from ablation therapy is much quicker than that from surgery. Most patients can return to their normal activities within a few days, whereas surgery may require weeks of recovery time.
- Reduced Risk: Because ablation is a less invasive procedure, the risk of complications such as bleeding, infection, and damage to surrounding tissue is much lower compared to surgery.
- Effective for Benign Nodules: For patients with benign thyroid nodules that cause discomfort or cosmetic concerns, ablation can provide effective relief without the need for extensive surgery, which is often reserved for malignant nodules or more complicated cases.
- Cosmetic Improvement: In addition to alleviating symptoms, ablation therapy can help reduce the size of thyroid nodules, improving the cosmetic appearance of the neck.
5. Key Differences Between Ablation and Surgery
When deciding between thyroid nodule ablation and surgery, it’s important to consider several factors including invasiveness, recovery time, success rates, costs, and long-term outcomes. Below is a comparison of both treatment options:
Procedure Comparison: Invasiveness, Recovery Time, and Success Rates
- Invasiveness:
Surgery typically involves making incisions in the neck, which can be more invasive and may require a general anesthetic. It often necessitates a hospital stay and a longer recovery period. Depending on the type of surgery, it can be a lobectomy (removal of one lobe) or a total thyroidectomy (removal of the entire thyroid).
Ablation therapy, on the other hand, is a minimally invasive procedure performed using a needle or catheter. It usually requires local anesthesia and is done on an outpatient basis, meaning patients can go home the same day. - Recovery Time:
The recovery time for surgery can range from several weeks to months, depending on the extent of the procedure. Surgical wounds need time to heal, and patients may experience significant discomfort and restriction in neck movement.
Ablation offers a much quicker recovery, with many patients able to resume normal activities within a few days. The procedure itself has a minimal recovery period, with only mild discomfort in some cases. - Success Rates:
Surgery has a high success rate in completely removing thyroid nodules or the thyroid gland itself, especially when the nodule is malignant. However, surgery does come with the risk of complications, including damage to the parathyroid glands or vocal cords.
Ablation therapy, such as radiofrequency ablation (RFA), is successful in reducing the size of benign thyroid nodules and alleviating symptoms like difficulty swallowing. However, it may not completely eliminate all nodules, and the long-term effectiveness for malignant nodules is still being studied.
Cost Comparison and Insurance Considerations
- Cost:
Surgery is typically more expensive due to hospital stays, anesthesia, and the surgical procedure itself. It may also involve additional costs for post-surgery care and follow-up visits.
Ablation therapy is generally less expensive because it is minimally invasive and doesn’t require the same level of hospital resources or recovery care. The cost will vary depending on the location and the type of ablation used. - Insurance Considerations:
Insurance coverage for surgery is generally well-established, especially for medically necessary procedures such as the removal of malignant thyroid nodules. However, some insurance plans may have restrictions or additional requirements for coverage.
Ablation therapy, while gaining acceptance, may not always be fully covered, especially in regions where it is considered a newer or less standard treatment option. Patients should consult with their insurance providers to confirm coverage for thyroid nodule ablation treatment.
Long-term Outcomes and Potential Side Effects
- Long-term Outcomes:
Surgery offers a permanent solution by removing the thyroid nodule or the thyroid gland itself. However, there may be long-term hormonal imbalances if the entire thyroid is removed, requiring lifelong thyroid hormone replacement.
Ablation therapy provides a non-permanent but effective solution for managing benign thyroid nodules. While the procedure can reduce the size of the nodule and alleviate symptoms, nodules may potentially regrow over time, requiring further treatment. - Potential Side Effects:
Surgery can have potential side effects such as scarring, changes in voice (due to damage to the vocal cords), and risks associated with anesthesia.
Ablation carries a lower risk of side effects, but patients may experience minor complications such as skin burns, hematoma (bruising), or temporary pain at the treatment site.
6. When Should You Consider Ablation Over Surgery?
Ideal Candidates for Ablation
Ablation is typically recommended for patients with benign thyroid nodules that are not causing cancer. It is an ideal option for those who want to avoid the invasiveness of surgery and have nodules causing symptoms like discomfort or cosmetic concerns. Additionally, ablation is suitable for patients who may have comorbid conditions that make surgery riskier or for those who want to avoid potential long recovery times associated with traditional surgery.
Situations Where Surgery Might Still Be Preferred
Surgery remains the preferred option when:
- Thyroid nodules are suspected to be malignant, requiring a biopsy and removal of the tissue for definitive diagnosis and treatment.
- The size of the nodule is large and causing significant problems such as airway obstruction or pressure on surrounding structures.
- Ablation therapy is not effective for certain types of nodules, particularly if the nodule is very hard or large, or when other treatment methods fail.
Factors Influencing the Decision
Several factors influence the decision between ablation and surgery:
- Nodule size: Larger nodules or those that cause visible deformities may require surgery for removal.
- Symptoms: If the nodule causes significant symptoms, like difficulty swallowing or breathing, surgery may be the only option.
- Patient health: Patients with other medical conditions that could complicate surgery (e.g., heart disease) may prefer less invasive treatments like thyroid nodule ablation.
- Risk of malignancy: If there is a strong suspicion or confirmation of cancer, surgery is typically the preferred treatment.
while thyroid nodule ablation offers several benefits over traditional surgery, including quicker recovery and reduced risks, the choice of treatment depends on individual circumstances, such as the nature of the nodule, overall health, and personal preferences.
For patients in Mumbai, those considering thyroid nodule ablation may consult with specialized centers like Midas Care Clinic, which offer advanced ablation treatments for thyroid nodules.
7. Pros and Cons: Ablation vs. Surgery
When comparing thyroid nodule ablation and surgery, each treatment option comes with its unique set of advantages and disadvantages.
Pros of Ablation
- Minimally invasive: Ablation therapy, such as radiofrequency ablation (RFA) or laser ablation, requires only small incisions or needle insertions, making it a minimally invasive option. This leads to less trauma and lower complication rates compared to surgery.
- Shorter recovery: Because the procedure is less invasive, recovery times for ablation are typically much shorter, with many patients resuming their normal activities within a few days.
- Lower risks: Ablation involves fewer risks compared to surgery. There’s no risk of general anesthesia, and patients generally experience less pain and discomfort post-treatment.
- Effective for benign nodules: Ablation therapy works especially well for benign thyroid nodules, offering significant reduction in size and symptoms such as difficulty swallowing or neck discomfort.
Cons of Ablation
- Limitations based on nodule type: Ablation may not be suitable for all types of thyroid nodules, particularly for large or very hard nodules, or those with suspected malignancy.
- Potential for recurrence: Although ablation can shrink thyroid nodules, there is a possibility that the nodule may regrow over time, requiring additional treatments.
- Not a definitive solution for malignancy: In cases where a thyroid nodule is cancerous, ablation may not be effective, and surgery would be necessary for a definitive solution.
Pros of Surgery
- Comprehensive treatment: Surgical options, such as lobectomy or total thyroidectomy, can provide a comprehensive solution, especially in cases of malignant thyroid nodules.
- Potential for definitive resolution: For malignant nodules, surgery can offer a definitive treatment by completely removing the affected tissue.
- Long-term effectiveness: Surgery is often a one-time solution, eliminating the nodule entirely, which is particularly important for patients with cancerous nodules.
Cons of Surgery
- Longer recovery: Surgery requires a longer recovery time, which may involve several weeks of rest and avoiding physical activity.
- Higher risks: Surgical procedures carry the risks associated with anesthesia, wound infections, and complications such as damage to the parathyroid glands or vocal cords.
- Scarring: Since surgery involves incisions, it often leaves visible scarring on the neck, which can be a cosmetic concern for some patients.
8. What to Discuss with Your Doctor
Before making a decision between ablation and surgery, it is crucial to have an in-depth discussion with your healthcare provider to determine the best treatment plan for your situation.
Questions to Ask Your Healthcare Provider
- What type of thyroid nodule do I have (benign or malignant)?
- What are the risks and benefits of each treatment option based on my individual health?
- How long will the recovery process take for each treatment?
- Are there any potential side effects or complications associated with either treatment?
- What are the costs and insurance considerations for each option?
Importance of Personalized Treatment Plans
Every thyroid nodule is unique, and treatment should be tailored to the patient’s specific condition. Your healthcare provider will assess factors such as nodule size, symptoms, and overall health to help guide the decision. It’s essential to understand the benefits and limitations of both thyroid nodule ablation and surgery in the context of your personal health needs.
Understanding Your Options Based on Individual Health Needs
Patients should consider their own health conditions, preferences, and the nature of the thyroid nodule when deciding between surgery and ablation. For example, individuals with other underlying health conditions may prefer the less invasive nature of ablation to avoid the risks associated with surgery. Similarly, patients with cancerous nodules may need to opt for surgery for definitive treatment.
9. Conclusion
In conclusion, both thyroid nodule ablation and surgery are viable options for treating thyroid nodules, but they offer different advantages and challenges. Ablation provides a less invasive and quicker recovery option, while surgery remains the gold standard for addressing malignant nodules and offering a more permanent solution.
It is essential to consult with a qualified healthcare provider to determine the best treatment plan based on your individual situation. By understanding the differences between these treatments, you can make an informed decision and take control of your health. If you are considering thyroid nodule ablation in Mumbai, consider visiting reputable centers like Midas Care Clinic, where professionals can guide you toward the best course of action for your thyroid health.

