What is FNAC Test?
Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC) is a simple and minimally invasive medical test used to examine lumps, swellings, or unusual growths in the body. Doctors perform this test to determine whether a lump is benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous) and to diagnose infections or inflammatory conditions.
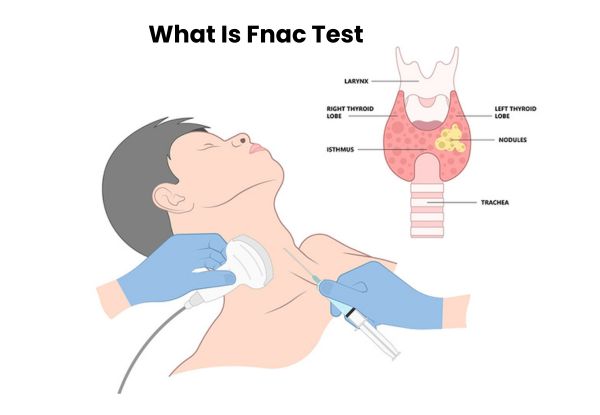
During the procedure, a thin, hollow needle is inserted into the affected area to extract a small sample of cells or fluid. This sample is then examined under a microscope to identify abnormalities. FNAC is a widely used diagnostic tool because it is quick, safe, and does not require surgery.
Why is FNAC Recommended?
Doctors suggest an FNAC test when they find an unexplained lump or swelling that needs further evaluation. It is particularly useful for:
- Detecting tumors in different body parts.
- Confirming infections like tuberculosis.
- Assessing cysts or abscesses in soft tissues.
- Investigating swollen lymph nodes that may indicate infections or cancers.
Common Areas Where FNAC is Performed
The test is commonly conducted on:
- Breast: To check for lumps or tumors.
- Thyroid gland: To evaluate nodules and determine if they are benign or cancerous.
- Lymph nodes: To diagnose infections, lymphoma, or metastatic cancer.
- Lungs: To assess abnormalities detected in imaging tests.
- Salivary glands: To investigate swelling or tumors.
By providing fast and accurate results, FNAC plays a crucial role in diagnosing various medical conditions. It helps doctors decide whether further tests, biopsies, or treatments are necessary.
Why is FNAC Test Done?
Doctors recommend the FNAC test when they need to evaluate a lump or abnormal tissue growth in the body. This test helps in diagnosing various medical conditions quickly and safely. Since it is a minimally invasive procedure, it is often preferred over surgical biopsies.
When is FNAC Recommended?
A fine needle aspiration biopsy is commonly used in the following cases:
- Detecting Cancer: If a lump is suspected to be malignant, FNAC helps confirm the presence of cancer cells. It is often used for detecting breast cancer, thyroid cancer, and lymphomas.
- Diagnosing Infections: FNAC is useful in diagnosing infections like tuberculosis. A fnac test for TB is performed when a doctor suspects an infection in lymph nodes or lungs.
- Evaluating Cysts and Abscesses: Some lumps contain fluid instead of solid tissue. FNAC can determine whether a swelling is a cyst or an abscess that requires drainage or medical treatment.
- Assessing Unexplained Swellings: FNAC is used for lumps in the neck, armpits, groin, and salivary glands to rule out infections or tumors.
- Monitoring Recurring Growths: If a patient has had previous tumors, FNAC helps in detecting regrowth or changes in tissue.
FNAC Test for Cancer
A fnac test for cancer is one of the most effective ways to detect malignancies in their early stages. The test identifies abnormal cell structures that indicate cancerous growths, allowing for prompt medical intervention.
By providing a quick and accurate diagnosis, FNAC test helps doctors decide on the next steps, whether it’s further testing, treatment, or surgery.
FNAC Test Procedure
How is FNAC Performed?
The FNAC procedure is a simple and minimally invasive technique that helps doctors examine lumps or abnormal growths in the body. The test is quick, usually painless, and does not require anesthesia. It is often performed in a clinic or diagnostic center without the need for hospitalization.
Step-by-Step Process of FNAC
- Preparation
- The doctor cleans the skin around the lump or swelling to prevent infection.
- In some cases, a local anesthetic may be applied to reduce discomfort.
- Insertion of the Fine Needle
- A thin, hollow fnac needle is gently inserted into the lump or affected area.
- The needle is usually smaller than those used for blood tests, making the procedure less painful.
- Cell Collection
- The doctor moves the needle back and forth to collect a sample of cells or fluid.
- If the lump is deep inside the body, ultrasound or CT guidance may be used to ensure accuracy.
- Sample Processing
- The collected sample is placed on a glass slide and treated with special stains.
- A pathologist examines the sample under a microscope to detect any abnormalities.
- Completion & Aftercare
- The procedure takes about 10-15 minutes.
- Patients can resume normal activities immediately, though minor bruising or discomfort may occur.
Why is FNAC Considered a Reliable Diagnostic Tool?
- It is quick and minimally invasive compared to surgical biopsies.
- The test provides fast results, usually within 24-48 hours.
- It helps in early detection of infections, tumors, and other conditions.
A fine needle aspiration biopsy is an important diagnostic tool that helps doctors make informed decisions about further testing or treatment.
Is FNAC Test Painful?
Many people worry about discomfort during medical tests, and it is natural to ask, “Is FNAC test painful?” The FNAC test is a minimally invasive procedure that involves inserting a thin needle into the lump or affected area to extract a sample of cells. The level of pain is generally mild and temporary, similar to a routine blood test.
What Does FNAC Feel Like?
- Mild Stinging Sensation: Some patients may feel a small pinch or a slight sting when the needle is inserted.
- Minimal Discomfort: As the doctor moves the needle inside the lump, there might be a slight pressure, but it is not severe.
- No Need for Anesthesia: Since the procedure is quick and involves a fine needle, local anesthesia is usually not required.
FNAC Pain vs. Biopsy Pain
A traditional biopsy involves a larger needle or a minor surgical cut, which can cause significant pain and require stitches. In contrast, an FNAC test for neck lumps, lymph nodes, and other body parts is far less painful.
| Comparison | FNAC Test | Surgical Biopsy |
| Needle Size | Very thin | Larger |
| Pain Level | Mild discomfort | Moderate to high |
| Healing Time | No downtime | May take a few days |
| Scarring | No visible marks | Small scar possible |
| Anesthesia Needed? | No | Usually required |
Does FNAC Cause Pain After the Test?
Most patients feel fine immediately after the test. There may be slight soreness or bruising, especially in sensitive areas like the neck or lymph nodes, but this usually fades within a few hours. Applying an ice pack can help if there is mild swelling.
For those undergoing an FNAC test for neck lumps or FNAC lymph node tests, the discomfort is similar to getting a vaccination and does not interfere with daily activities.
How to Prepare for an FNAC Test?
Preparing for an FNAC test is simple and does not require major lifestyle changes. However, following a few basic guidelines can help ensure accurate results and a smooth testing process.
Do You Need to Fast Before an FNAC Test?
In most cases, fasting is not required before an FNAC test. Patients can eat and drink as usual unless the doctor provides specific instructions. However, if the test involves certain organs like the liver or pancreas, fasting may be necessary. Always confirm with your doctor before the procedure.
Can Medications Affect FNAC Results?
Some medications, especially blood thinners like aspirin or warfarin, may slightly increase the risk of bruising or bleeding at the test site. Patients should inform their doctor about any medications they are taking before undergoing the test.
For conditions like tuberculosis, FNAC is often used to collect samples from lymph nodes or affected tissues to confirm the infection.
Other Preparation Tips:
- Wear loose clothing to allow easy access to the test area.
- Avoid applying creams, lotions, or powders on the skin near the lump.
- Inform your doctor about any allergies to antiseptics or anesthesia, if applicable.
- Stay relaxed FNAC is a quick and safe procedure with minimal discomfort.
For patients undergoing an FNAC blood test or an FNAC test for tuberculosis, it is important to follow the doctor’s specific instructions to ensure accurate diagnosis and effective treatment planning.
FNAC Test Results & Interpretation
How to Read an FNAC Report?
Understanding an FNAC report is important for determining the next steps in medical care. The report provides insights into whether the collected sample contains normal, abnormal, or inconclusive findings.
What Do FNAC Results Mean?
- FNAC Test Normal Report
- If the report indicates no abnormal cells, it means the lump or swelling is benign (non-cancerous).
- The patient may not need further testing unless symptoms persist or worsen.
- FNAC Test Positive Means
- A positive FNAC test means the sample contains abnormal or cancerous cells.
- Further testing, such as a core biopsy or imaging, may be required to confirm the diagnosis and plan treatment.
- FNAC Test Negative Means
- A negative FNAC test suggests no signs of malignancy or infection in the sample.
- However, in some cases, a repeat FNAC or additional tests may be needed if symptoms persist.
Inconclusive FNAC Reports
Sometimes, an FNAC report may be inconclusive due to:
- Insufficient sample collection (too few cells to analyze).
- Unclear cell characteristics that require further testing.
- Contamination or errors in sample handling.
In such cases, doctors may recommend a repeat FNAC test or a more detailed biopsy for accurate diagnosis.
What Happens After Receiving an FNAC Report?
- If the report is normal, routine monitoring may be enough.
- If it is abnormal, doctors will suggest further tests or a treatment plan based on the findings.
- If results are unclear, the patient may need a repeat FNAC or another diagnostic procedure.
Interpreting FNAC reports correctly allows doctors to make informed decisions about treatment and follow-up care.
Can FNAC Test Detect Cancer?
The FNAC test is an effective diagnostic tool that helps in detecting cancerous and non-cancerous growths. However, while it provides quick and valuable insights, it has some limitations in confirming cancer definitively.
FNAC’s Accuracy in Detecting Cancer
A cancer FNAC test report is considered highly accurate when it identifies malignant (cancerous) cells. The test is particularly useful for diagnosing cancers in the:
- Breast (breast lumps and tumors)
- Thyroid (thyroid nodules)
- Lymph nodes (lymphomas and metastatic cancers)
- Salivary glands (unusual swellings)
When performed correctly, FNAC can detect abnormal cell changes in a lump, helping doctors decide whether a biopsy or further testing is needed.
Limitations of FNAC in Cancer Diagnosis
Despite its usefulness, FNAC has limitations, especially when diagnosing certain cancers.
- Sampling Errors: If the collected sample is too small or does not include the affected cells, results may be inconclusive.
- Lack of Tissue Architecture: Unlike a core biopsy, FNAC does not provide a detailed view of tissue structure, which is important in diagnosing certain cancers.
- FNAC Correlation Means Further Tests May Be Needed: If FNAC results suggest abnormal cells but lack clarity, doctors may recommend a repeat FNAC, imaging tests, or a more detailed biopsy.
When is FNAC Not Enough for Cancer Diagnosis?
- If a cancer FNAC test report is inconclusive or suspicious, additional tests are required.
- In some cases, a pathologist may request FNAC correlation, meaning the FNAC results need to be compared with other diagnostic tests like MRI, CT scans, or histopathology.
While FNAC is a valuable first step in detecting cancer, a final diagnosis often requires further testing to confirm malignancy and determine the best treatment approach.
FNAC Test vs. Biopsy Test: Which One is Better?
When evaluating lumps or abnormal tissue growth, doctors use FNAC biopsy and surgical biopsy to diagnose conditions. While both tests help detect benign and malignant growths, they differ in terms of procedure, accuracy, and invasiveness.
FNAC Test vs. Biopsy Test : Key Differences
| Feature | FNAC (Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy) | Surgical Biopsy |
| Procedure | A thin needle is used to extract cell samples. | A small tissue section is removed surgically. |
| Pain Level | Minimal pain, no anesthesia required. | Can be painful, requires local or general anesthesia. |
| Invasiveness | Less invasive, no stitches needed. | More invasive, may require stitches. |
| Recovery Time | Immediate recovery, no downtime. | Healing may take a few days. |
| Accuracy | Useful for detecting abnormal cells but may not provide full tissue structure. | Provides a complete view of tissue, increasing diagnostic accuracy. |
| When Used? | Initial screening for lumps, cysts, infections. | Used when FNAC results are inconclusive or further analysis is needed. |
Advantage of FNAC Over Biopsy
- Quick and less invasive: FNAC can be performed in minutes, and the patient can resume daily activities immediately.
- Minimal discomfort: Since a fine needle aspiration biopsy uses a thin needle, the pain is mild compared to a surgical biopsy.
- Lower risk of complications: There is little to no bleeding or scarring.
Disadvantage of FNAC Compared to Biopsy
- Less detailed analysis: FNAC extracts only cells, whereas a biopsy provides complete tissue architecture.
- Possibility of inconclusive results: Sometimes, the collected sample may not be enough, requiring a repeat FNAC or a biopsy.
- Cannot always confirm cancer type: A biopsy may be needed to determine the exact nature of a tumor.
When Do Doctors Prefer FNAC Over a Biopsy?
Doctors usually recommend FNAC or biopsy when:
- The lump is small, superficial, and accessible.
- A quick diagnosis is required to decide on further tests.
- The risk of complications from a surgical biopsy is high.
However, when FNAC results are unclear or do not provide enough information, a surgical biopsy is the next step for a definitive diagnosis.
Risks and Side Effects of FNAC Test
The FNAC test is considered a safe and minimally invasive procedure, but like any medical test, it carries some minor risks. Since it involves inserting a thin needle into a lump or swelling, mild discomfort may occur. However, serious complications are extremely rare.
Common FNAC Test Side Effects
Most patients experience little to no side effects, but some may notice:
- Mild Pain or Discomfort: The test site may feel sore for a few hours after the procedure.
- Swelling or Bruising: Some minor swelling can occur, especially if multiple attempts are needed to collect the sample.
- Minor Bleeding: A small amount of bleeding may be seen, particularly in patients on blood thinners.
These symptoms typically subside within a day, and no special treatment is required. Applying an ice pack and avoiding excessive movement of the tested area can help reduce discomfort.
Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology Risks: When to Consult a Doctor?
Although rare, certain signs may indicate a complication that requires medical attention. Seek a doctor’s help if you experience:
- Persistent or increasing pain that does not improve within 24 hours.
- Excessive swelling or redness around the test site.
- Signs of infection, such as fever or pus formation.
- Uncontrolled bleeding at the test site.
Is FNAC a Risky Procedure?
Compared to other diagnostic procedures, the FNAC test is very safe. Since fnac pathology involves only a small sample collection, it does not cause serious damage to surrounding tissues. The benefits of early and accurate diagnosis outweigh the minor risks associated with the test.
Most patients recover immediately after the test and can return to their normal routine without restrictions.
FNAC Test Cost in India
The cost of an FNAC test in India starts from Rs 800 to Rs 4000 it varies depending on several factors, including the city, healthcare facility, and whether imaging guidance is used during the procedure.
Estimated Cost Range in Different Cities
- Delhi: Prices start around ₹1,540.
- Mumbai: The cost ranges from ₹400 to ₹3,000.
- Bangalore: Starting prices are approximately ₹918.
- Hyderabad: FNAC tests are available from ₹1,100.
For CT-guided FNAC tests, which provide imaging assistance during the procedure, the costs are generally higher. In Mumbai, for example, CT-guided FNAC tests start at ₹12,000.
Factors Affecting FNAC Test Price
Several elements influence the FNAC test price in India:
- Type of Facility: Private hospitals and diagnostic centers may charge more than government institutions.
- Location: Metropolitan areas often have higher costs compared to smaller cities.
- Guidance Method: Procedures using imaging techniques like ultrasound or CT guidance are more expensive due to the advanced technology involved.
- Additional Services: Home sample collection or expedited reporting can increase the overall cost.
It’s advisable to consult with local diagnostic centers or hospitals to obtain accurate pricing tailored to your specific needs.
Common Myths & Misconceptions About FNAC
Many people have misconceptions about FNAC (Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology) due to a lack of information. Below are some of the most common myths and the truth behind them.
Does FNAC Spread Cancer?
One of the most common fears is that FNAC spreads cancer cells. However, there is no scientific evidence to support this claim. FNAC uses a very fine needle, which minimizes the risk of cell displacement. Studies have shown that FNAC is a safe procedure that does not increase cancer spread.
Is FNAC Always Accurate?
While FNAC test accuracy is high, it is not 100% foolproof. The results depend on factors such as:
- The quality of the sample collected
- The experience of the pathologist analyzing the sample
- The location and type of the lesion
In some cases, FNAC may provide inconclusive results, requiring a repeat test or a biopsy for further analysis.
Is FNAC Better Than a Biopsy?
Both FNAC and biopsy serve different purposes:
- FNAC is less invasive, faster, and suitable for preliminary diagnosis.
- Biopsy provides a more detailed tissue structure, making it more reliable for definitive cancer diagnosis.
Doctors choose FNAC or biopsy based on the patient’s condition and the type of tissue being examined.
Understanding FNAC in Medical Terms
- FNAC Definition: A diagnostic procedure that uses a fine needle to extract cell samples from a lump or swelling for microscopic examination.
- FNAC Medical Abbreviation: FNAC stands for Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology. It is a commonly used term in pathology and diagnostic medicine.
By addressing these common misconceptions, patients can feel more confident about undergoing FNAC when recommended by their doctor.
Latest Advances in FNAC Technology
Recent developments in Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC) are enhancing diagnostic precision and patient care.
Artificial Intelligence Enhancements
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is playing a significant role in improving FNAC accuracy. By analyzing cytology images, AI assists pathologists in identifying subtle patterns that might be overlooked. For instance, in thyroid FNAC, AI-based image analysis has demonstrated high accuracy, aiding in more reliable diagnoses.
Advancements in Guided Procedures
Guided FNAC procedures, such as those using ultrasound or CT imaging, have improved sample collection. These techniques allow for precise needle placement, especially in challenging areas.
Studies have shown that ultrasound-guided FNAC reduces the rate of inadequate samples compared to conventional methods, leading to more accurate diagnoses.
These innovations are making FNAC a more effective tool in medical diagnostics.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is the full form of FNAC?
Ans: The FNAC full form is Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology. It is a minimally invasive diagnostic procedure used to examine lumps, tumors, and swellings. The FNAC full form in medical terminology refers to a cytology-based test that helps detect abnormal cells.
Q2: How long does it take to get FNAC test results?
Ans: The FNAC test report time typically ranges from 24 to 48 hours. In some cases, it may take longer if special staining or further analysis is required.
Q3: Is FNAC better than a biopsy?
Ans: The choice between FNAC vs biopsy depends on the case:
- FNAC is faster, less invasive, and requires no stitches.
- A biopsy provides a more detailed tissue structure, making it better for definitive cancer diagnosis.
Both tests play important roles in diagnosing abnormalities. A fine needle aspiration biopsy is often the first step before a surgical biopsy is considered.
Q4: Can FNAC test detect all types of tumors?
Ans: A FNAC test for cancer can detect many types of tumors, but not all. Certain deep-seated or complex tumors may require a core biopsy for a more detailed tissue analysis. A cancer FNAC test report helps doctors determine whether further testing is necessary.
Q5: What should I do if my FNAC results are inconclusive?
Ans: If FNAC test results are inconclusive, doctors may recommend:
- A repeat FNAC test
- Additional imaging tests (CT scan, MRI)
- A core or surgical biopsy
A FNAC test negative means no abnormal cells were found, while a FNAC test positive means cancerous or abnormal cells were detected. However, false negatives can occur, requiring further investigation.
Q6: What is the cost of FNAC in Mumbai and Vasai?
Ans: The FNAC test price in Mumbai varies between ₹400 to ₹3,000, depending on the facility and whether it includes imaging guidance. In Vasai, the cost may be slightly lower. If you’re searching for an FNAC test in Vasai or an FNAC test near me, consult local diagnostic centers for exact pricing.
Q7: Can FNAC test diagnose tuberculosis?
Ans: Yes, an FNAC test for TB is commonly performed when tuberculosis is suspected in lymph nodes or affected tissues. The FNAC test for tuberculosis helps confirm TB by detecting granulomatous inflammation and Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria in the sample.
Q8: Are there any side effects of FNAC?
Ans: The FNAC pathology procedure is generally safe, with minimal risks. However, some fine needle aspiration cytology risks include:
- Mild pain or bruising at the test site
- Temporary swelling
- Minimal bleeding
Serious complications are rare, and most side effects resolve within 24 hours.
Q9: What happens if FNAC test results are abnormal?
Ans: If your FNAC test results are abnormal, further medical evaluation is needed. A doctor will interpret the FNAC report and may recommend additional tests. In some cases, an FNAC correlation means the results should be compared with other diagnostic findings for accuracy.
Q10: Where can I get an FNAC test in Vasai?
Ans: If you’re looking for an FNAC test in Vasai, Midas Care Clinic is one of the best diagnostic centers in Vasai, offering accurate and reliable FNAC testing.
Conclusion
The FNAC test is a minimally invasive diagnostic procedure used to detect tumors, infections, and other abnormalities in various body parts like the thyroid, breast, and lymph nodes. It provides quick and reliable results, helping doctors determine the next steps in treatment.
While safe and effective, FNAC has certain limitations, and additional tests may be required for a definitive diagnosis. Understanding its procedure, accuracy, and results ensures better decision-making for patients and healthcare providers.

